Manila Network Plugins: Simple Neutron Port Binding Network Plugin¶
Simple Neutron Port Binding Network Plugin: This plugin is very
similar to the simple Neutron network plugin, the only difference is
that this plugin can enforce port-binding. Port binding profiles from
the manila configuration file are sent to Neutron at the time of
creating network ports for the purpose of creating ONTAP LIFs. This
allows network agents to bind the ports based off these profiles.
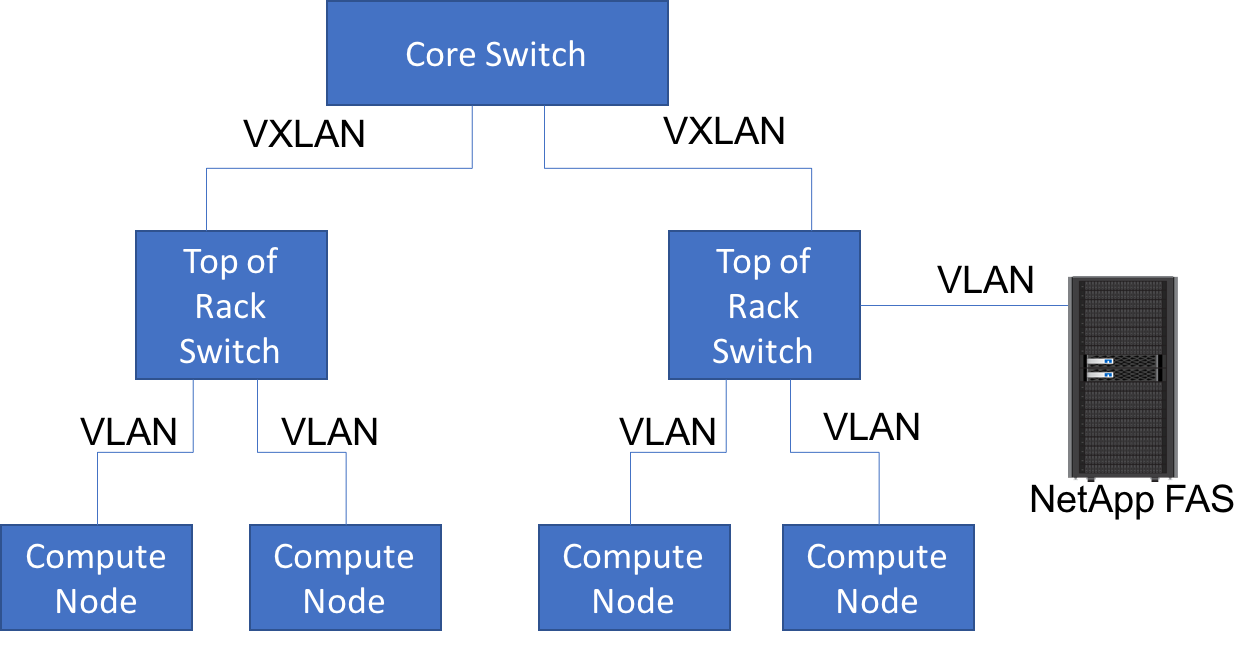
When using multiple top of the rack switches to connect different
compute nodes, this plugin is also capable of performing Hierarchical
Port Binding. Administrators would configure the VLAN-only neutron
network to use in the backend stanza of the manila.conf and
tenants must create their own share network objects to allow the
NetApp driver to create VServers connected to this network.
Tenants must not specify Neutron network information when creating share network objects. Manila will derive values for segmentation protocol, IP address, netmask and gateway from Neutron when creating a new share server.
In this configuration, administrators set up a single neutron network,
and Manila will send any binding profiles configured in manila.conf
to Neutron while creating ports on the network. As noted prior, Neutron
may be configured with a hardware switch to provide tenant networks with
access to devices connected to the hardware switch. You may use the
switch vendor’s ML2 mechanism driver to dynamically allocate segments
corresponding to the segments created on the OpenStack compute hosts by
OVS. This port binding network plugin is crucial to ensure that port
binding occurs at the mechanism driver. Verify with your switch vendor
if they support binding profiles. While most vendors support port
binding, some may not support the “baremetal” vnic_type. Use of this
plugin is preferable when using a hierarchical virtual network that uses
different network segments. These segments can be of different network
types (ex: VLAN within the rack and VXLAN between the top-of-rack and
core switches). To set up the simple Neutron port binding network
plugin, the following options should be added to the driver-specific
stanza within the Manila configuration file (manila.conf). The
Neutron binding profile in this example is for a Cisco Nexus 9000
switch:
network_api_class = manila.network.neutron.neutron_network_plugin.NeutronBindSingleNetworkPlugin
neutron_net_id = 37fb9f7e-4ffe-4900-8dba-c6d4251e588e
neutron_subnet_id = 447732be-4cf2-42b0-83dc-4b6f4ed5368c
neutron_host_id = netapp_lab42
neutron_vnic_type = baremetal
neutron_binding_profiles = phys1
[phys1]
neutron_switch_id = 10.63.152.254
neutron_port_id = 1/1-4
neutron_switch_info = switch_ip:10.63.152.254
The following table lists the configuration options available for the Simple Neutron Port Binding network plugin:
| Option | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
neutron_net_id |
Required | Specify the ID of a Neutron network from which ports should be created. | |
neutron_subnet_id |
Required | Specify the ID of a Neutron subnet from which ports should be created. | |
neutron_host_id |
Optional | Perceived system hostname | Hostname of the node where the manila-share service is running, configured with the NetApp backend. |
neutron_vnic_type |
Optional | baremetal | Virtual NIC type for the ports created by Neutron on this network. Supported type is “baremetal” |
neutron_binding_profiles |
Optional | Comma separated list of binding profile sections. Each of these sections can contain specific switch information and they can be shared amongst different backends. |
Table: Configuration options for Simple Neutron Port Binding Network Plugin
This document is licensed under Apache 2.0 license.